Advance
Alignment Issue
指令的操作数的地址没有对齐,则会报错(段错误),例如AVX指令集需要32位内存对齐(即该操作数的地址需要被32整除)
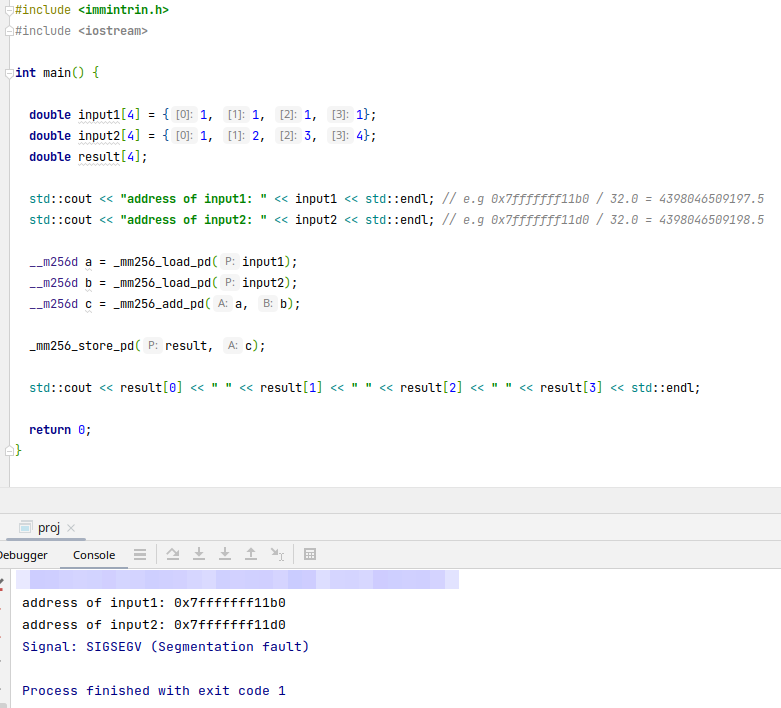
指定变量的内存对齐
// e.g. 指定分配的内存地址能被32整除
// 等价于: __attribute__ ((aligned (32))) double input1[4] = {1, 1, 1, 1};
alignas(64) double input1[4] = {1, 1, 1, 1};
查看当前CPU支持的指令集
cat /proc/cpuinfo
GenericProgramming
迭代器作为算法和数据的桥梁
支持多种类型的算法,比如
std::sort();基于容器的算法标准库:
algorithm,numeric,ranges
Q&A
为什么算法的实现不都采用类内函数的方式来实现?
C++中内建数据类型不支持方法
计算逻辑存在相似性,避免重复定义
MetaProgramming
设计在编译期运行的代码
判断某个类型的属性
#include <iostream>
#include <type_traits>
using namespace std;
int main() {
cout << boolalpha << endl;
cout << "int[2] is copy-assignable? " << is_copy_assignable<int[2]>::value << endl;
}
得到某个类型的大小
sizeof(type/object):用来获取对象或类型所对应的对象的大小(单位:字节)sizeof无法测动态数组的内存大小,因为得到的只是指向首元素的指针而不是数组名(数组名也是个地址,但其类型指向整个数组)"Used when actual size of the object must be known"
auto ptr = new bool[40];
cout << sizeof(ptr) << endl; // 8
cout << sizeof(*ptr) << endl; // 1(获得指向首元素的对象,并得其大小)
bool ptr2[40];
cout << sizeof(ptr2) << endl; // 40 (sizeof不会触发数组类型到指针的类型转换)
// sizeof(vector)为24:对应的元素为三个指针(3×8字节):_M_start, _M_finish, _M_end_of_storage
判断两个变量是否是相同类型/某个变量是否某个类型
#include <type_traits>
using namespace std;
int main() {
vector<int> arr(5);
// 注意使用尖括号
cout << is_same_v<decltype(arr.size()), unsigned long> << endl;
// c11判断类型
int a[3] = {1, 2, 3};
cout << typeid(a).name() << endl;
// c17判断类型是否相同(type_traits)
cout << is_same_v<decltype(a), int *> << endl;
}
Reference
ROS Eigen Alignment issueTroubleshooting.html)
Q&A
为什么设置左闭右开区间作为规范?
在实践过程中发现左闭右开和左开右闭,都能够实现区间相减(右区间-左区间)而得到元素的个数
若要区间包含上自然数0时,左开右闭的话会让区间下界包含非自然数
Off-By-One Error
要构建一个120块石头的时间金字塔,每隔十年放一块石头。共需要多少年完成?
共有120块石头,放了120次,间隔了119次,耗时1190年
一年级到六年级读完,要多少年?
[1, 7) 共跨越6个年级,每个年级需要读1年,共6年
元素(序号2)和元素(序号6)之间相差多少元素:(2, 6) 相差4-1=3个元素
区间和元素个数
区间 |
区间元素个数 |
|---|---|
|
|
|
|
|
|