CudaPractice
语法
原文档已非常详细,此处列出踩过坑的部分
返回值
.cu文件的主函数需要返回 int,而不能是void;核函数的返回值为void
关键词(identifier)
修饰函数
__global__:告诉编译器,这个函数是在device上执行的,返回类型必须是void,不支持可变参数参数,不能成为方法。注意用此修饰的核函数是异步的,即CPU不会等待GPU执行完才执行下一步。__device__:在device上执行,仅可以从device中调用,不可以和__global__同时用。__host__:在host上执行,仅可以从host上调用,一般省略不写,不可以和__global__同时用,但可和__device__同时使用,此时函数会在device和host上都进行编译。
修饰变量
__device__:创建在d
调用核函数
// <<<numBlocks, threadsPerBlock>>>
// 创建6个线程块,每个线程块含有18个线程
add<<<6, 18>>>(dev_a, dev_b, dev_c);
术语
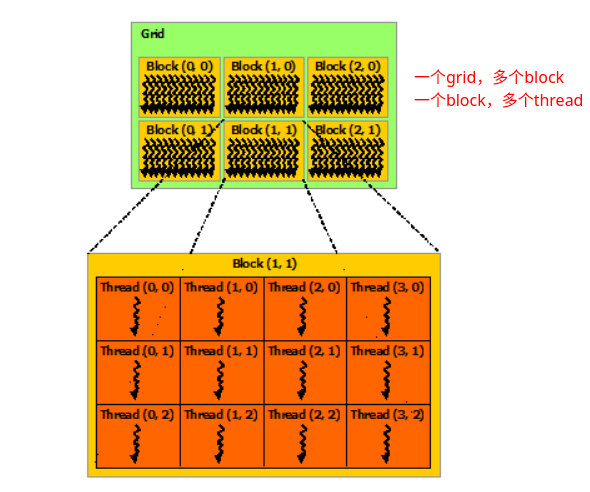
cu file:又称为kernels,能并行运行在N卡的处理单元上。kernels由nvcc编译,更多的命令行选项说明可参考here;需区别于kernel functiondevice/host:GPU和其内存/CPU和其内存kernels:核函数,在GPU上执行的函数,能在N个GPU线程中并行地执行这个函数grid,block,sm: 多个线程可以组成一个block,多个block组成一个grid,block由一个sm(流式多处理器)管理
cuda编程模型(software)
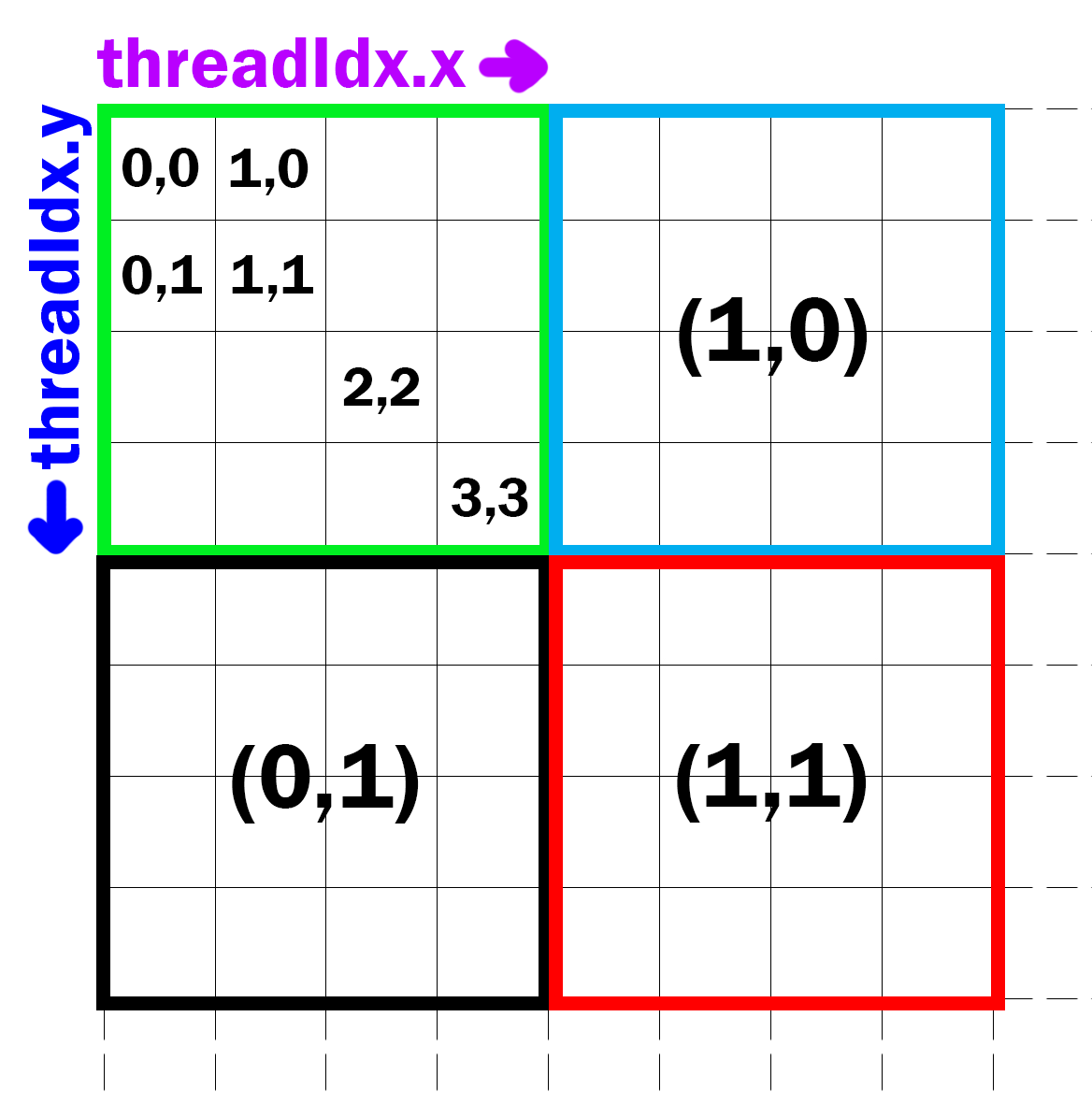
线程索引
每个线程都在一个线程块(block)中:每个线程都有一个thread ID,对应的内置变量为三维向量
threadIdx。对于二维线程块:(Dx, Dy),线程(x, y) 的ID为(x + y Dx),对于三维线程块:(Dx, Dy, Dz),线程 (x, y, z) 的ID为(x + y Dx + z Dx Dy)
备注
线程块=线程+共享内存
一个线程块含一个共享内存
每个线程块都在一个线程格(grid)中:每个线程块都有一个block ID,对应的内置变量为
blockDim
调试技巧
捕获错误
#include <iostream>
static void CheckCudaError(cudaError_t err, const char *file, int line) {
if (err != cudaSuccess) {
printf("[%s@%d]%s in %s:%d\n", cudaGetErrorName(err), err,
cudaGetErrorString(err), file, line);
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
}
}
#define CHECK_CUDA_ERROR(err) (CheckCudaError(err, __FILE__, __LINE__))
// e.g. CHECK_CUDA_ERROR(cudaFree(dev_c));
备注
clion配合 awesome console 插件的快速跳转报错位置就很赞
cudaError官方文档诊断
案例1:核函数返回代码为cudaErrorNoKernelImageForDevice:The error here comes about due to the fact that a CUDA kernel must be compiled in a way that the resulting code (PTX, or SASS) is compatible with the GPU that it is being run on:添加编译选项,指明生成的代码所支持的计算架构
set(CUDA_NVCC_FLAGS ${CUDA_NVCC_FLAGS} -gencode arch=compute_50,code=sm_50)
案例2:Cuda Runtime (an illegal memory access was encountered): invalid argument:对同一空间进行了多次的FREE
printf
printf可以在核函数中执行,但需要核函数顺利执行才会有输出
内存管理
裸指针
示例(abstract from autoware@idar_apollo_instance_segmentation)
// 创建
int nbBindings = mTrtEngine->getNbBindings();
mTrtCudaBuffer.resize(nbBindings);
mTrtBindBufferSize.resize(nbBindings);
for (int i = 0; i < nbBindings; ++i) {
Dims dims = mTrtEngine->getBindingDimensions(i);
DataType dtype = mTrtEngine->getBindingDataType(i);
int64_t totalSize = volume(dims) * maxBatchSize * getElementSize(dtype);
mTrtBindBufferSize[i] = totalSize;
mTrtCudaBuffer[i] = safeCudaMalloc(totalSize);
if (mTrtEngine->bindingIsInput(i)) {
mTrtInputCount++;
}
}
// 析构
for (auto & item : mTrtCudaBuffer) {
cudaFree(item);
}
备注
对应的代码所有使用锁页内存,TRT的显存是**根据TRT模型的输入和输出进行动态分配**的,没有写死
智能指针
使用自定义智能指针管理内存,而不用时刻注意调用cudaFree
示例
auto a = cuda::make_pin_unique<int[]>(N);
auto b = cuda::make_pin_unique<int[]>(N);
auto c = cuda::make_pin_unique<int[]>(N);
cuda::unique_gpu_ptr<int[]> dev_a = nullptr;
cuda::unique_gpu_ptr<int[]> dev_b = nullptr;
cuda::unique_gpu_ptr<int[]> dev_c = nullptr;
dev_a = cuda::make_gpu_unique<int[]>(N);
dev_b = cuda::make_gpu_unique<int[]>(N);
dev_c = cuda::make_gpu_unique<int[]>(N);
头文件:自定义内存回收逻辑
namespace cuda {
/**
* @brief 自定义内存回收逻辑
*/
struct deleter_gpu {
void operator()(void *p) const { CHECK_CUDA_ERROR(::cudaFree(p)); }
};
struct deleter_pin {
void operator()(void *p) const { CHECK_CUDA_ERROR(::cudaFreeHost(p)); }
};
template <typename T> using unique_gpu_ptr = std::unique_ptr<T, deleter_gpu>;
template <typename T> using unique_pin_ptr = std::unique_ptr<T, deleter_pin>;
// array type for gpu
template <typename T>
typename std::enable_if<std::is_array<T>::value, cuda::unique_gpu_ptr<T>>::type
make_gpu_unique(const std::size_t n) {
// e.g typename std::remove_extent<float[]>::type -> float;
// 取得数组中元素的类型
using U = typename std::remove_extent<T>::type;
U *p;
CHECK_CUDA_ERROR(::cudaMalloc(reinterpret_cast<void **>(&p), sizeof(U) * n));
return cuda::unique_gpu_ptr<T>{p};
}
// array type for pinned memory
template <typename T>
typename std::enable_if<std::is_array<T>::value, cuda::unique_pin_ptr<T>>::type
make_pin_unique(const std::size_t n) {
// e.g typename std::remove_extent<float[]>::type -> float;
// 取得数组中元素的类型
using U = typename std::remove_extent<T>::type;
U *p;
CHECK_CUDA_ERROR(::cudaMallocHost(reinterpret_cast<void **>(&p), sizeof(U) * n));
return cuda::unique_pin_ptr<T>{p};
}
#if 0
// 普通类型
template <typename T> cuda::unique_ptr<T> make_unique() {
T *p;
CHECK_CUDA_ERROR(::cudaMalloc(reinterpret_cast<void **>(&p), sizeof(T)));
return cuda::unique_ptr<T>{p};
}
#endif /*code block*/
} // namespace cuda
#endif // CUDA_UTILS_HPP
初始化内存
features_input_size_ = MAX_VOXELS * params_.max_num_points_per_pillar * 10 * sizeof(float);
checkCudaErrors(cudaMallocManaged((void **)&features_input_, features_input_size_));
checkCudaErrors(cudaMallocManaged((void **)¶ms_input_, 5 * sizeof(unsigned int)));
// Initializes or sets device memory to a value.
CHECK_CUDA_ERROR(cudaMemsetAsync(features_input_, 0, features_input_size_, stream_));
CHECK_CUDA_ERROR(cudaMemsetAsync(params_input_, 0, 5 * sizeof(float), stream_));
配置nvcc
find_package(CUDA REQUIRED)
# 以下command需要导入cuda模块
CUDA_DETECT_INSTALLED_GPUS(INSTALLED_GPU_CCS_1)
# 处理字符串
string(STRIP "${INSTALLED_GPU_CCS_1}" INSTALLED_GPU_CCS_2)
string(REPLACE " " ";" INSTALLED_GPU_CCS_3 "${INSTALLED_GPU_CCS_2}")
string(REPLACE "." "" CUDA_ARCH_LIST "${INSTALLED_GPU_CCS_3}")
SET(CMAKE_CUDA_ARCHITECTURES ${CUDA_ARCH_LIST})
set_property(GLOBAL PROPERTY CUDA_ARCHITECTURES "${CUDA_ARCH_LIST}")
set(CUDA_NVCC_FLAGS ${CUDA_NVCC_FLAGS} -gencode arch=compute_${CUDA_ARCH_LIST},code=sm_${CUDA_ARCH_LIST})
message("-- Autodetected CUDA architecture(s): ${INSTALLED_GPU_CCS_3}")
message("-- Added CUDA NVCC flags for: -gencode;arch=compute_${CUDA_ARCH_LIST},code=sm_${CUDA_ARCH_LIST}")
备注
torch模块已包含了该部分;设置arch/code这些编译选项是为了防止nvcc生成当前架构没有的指令数据传递
数据传输
传统的内存开辟和数据传输
int main() {
const unsigned int N = 1048576;
const unsigned int bytes = N * sizeof(int);
// step1: 开辟CPU内存
// malloc返回的是void*类型,需要强制转换为int*类型
int *h_a = (int *)malloc(bytes);
int *d_a;
// step2: 开辟GPU内存
// 传入的是(存放开辟空间地址)的空间的地址 i.e.地址的地址
cudaMalloc((void **)&d_a, bytes);
// 填值
memset(h_a, 0, bytes);
// step3: 数据传输 CPU->GPU->CPU
cudaMemcpy(d_a, h_a, bytes, cudaMemcpyHostToDevice);
cudaMemcpy(h_a, d_a, bytes, cudaMemcpyDeviceToHost);
return 0;
}
NOTE
cudaMemcpy (void *dst, const void *src, size_t count/*bytes*/, cudaMemcpyKind kind)
// cudaMemcpyKind kind:
// cudaMemcpyHostToDevice
// cudaMemcpyDeviceToHost
// cudaMemcpyDeviceToDevice
// cudaMemcpyDefault(比较少用)
备注
内存传输一般是同步(cpu-gpu)的
使用锁页内存(具体可参考here)
int main()
{
unsigned int nElements = 4*1024*1024;
const unsigned int bytes = nElements * sizeof(float);
// host arrays
float *h_aPageable;
float *h_aPinned;
// device array
float *d_a;
// CPU端
// 开辟可分页内存
h_aPageable = (float*)malloc(bytes);
// 开辟锁页内存
checkCuda( cudaMallocHost((void**)&h_aPinned, bytes) );
// GPU端
// 分配GPU内存
checkCuda( cudaMalloc((void**)&d_a, bytes) );
for (int i = 0; i < nElements; ++i) h_aPageable[i] = i;
memcpy(h_aPinned, h_aPageable, bytes);
// cleanup
cudaFree(d_a);
cudaFreeHost(h_aPinned);
free(h_aPageable);
return 0;
}
备注
GPU访问CPU内存,只能访问CPU锁页内存。如果开辟是可分页内存的话,CUDA驱动会开辟临时的CPU锁页内存。直接开辟锁页内存的话,就会少这样一部分开销(当然,CPU内存要足够,否则反而影响性能)。
获取GPU硬件信息
#include "book.h"
void Getinfo(void)
{
cudaDeviceProp prop;
int count = 0;
cudaGetDeviceCount(&count);
printf("\nGPU has cuda devices: %d\n", count);
for (int i = 0; i < count; ++i) {
cudaGetDeviceProperties(&prop, i);
printf("----device id: %d info----\n", i);
printf(" GPU : %s \n", prop.name);
printf(" Capbility: %d.%d\n", prop.major, prop.minor);
printf(" Global memory: %luMB\n", prop.totalGlobalMem >> 20);
printf(" Const memory: %luKB\n", prop.totalConstMem >> 10);
printf(" SM in a block: %luKB\n", prop.sharedMemPerBlock >> 10);
printf(" warp size: %d\n", prop.warpSize);
printf(" threads in a block: %d\n", prop.maxThreadsPerBlock);
printf(" block dim: (%d,%d,%d)\n", prop.maxThreadsDim[0], prop.maxThreadsDim[1], prop.maxThreadsDim[2]);
printf(" grid dim: (%d,%d,%d)\n", prop.maxGridSize[0], prop.maxGridSize[1], prop.maxGridSize[2]);
}
printf("\n");
}
/**
GPU has cuda devices: 1
----device id: 0 info----
GPU : NVIDIA GeForce 940MX
Capbility: 5.0
Global memory: 2004MB
Const memory: 64KB
SM in a block: 48KB
warp size: 32
threads in a block: 1024
block dim: (1024,1024,64)
grid dim: (2147483647,65535,65535)
**/
备注
nvidia设备的warp所包含的线程一般为32,而每个线程块最多的线程数为1024
原子操作
// 存值
int atomicExch(int* address, int val);
向量化类型
使用向量化类型(vector type)能生成具有更高带宽的指令,而提高运行速度(ref)。比如默认的读写指令只能进行4个字节的操作,那么对于16字节的数据,则需要执行4次指令。而float4这种向量化指令则能够只执行1次指令。
编程n步曲
明确模块的输入和输出,以明确哪些需要分配显存/CPU内存
python拓展库
除将cu文件编译为可执行文件外,还可以基于setup.py进行编译,将其构建为python可调用的拓展库(一些实例可参考
pcdet, pytorch API, pytorch extension turorial)以下案例节选自here
步骤一:将build/lib*目录下的.so文件copy到python文件的同级目录
python setup.py build
若想直接在setup.py的当前目录下生成拓展库,直接:
python setup.py build_ext -i
步骤二:执行程序
python python test_extension.py
NOTE
ImportError: libc10.so: cannot open shared object file: No such file or directory:在python文件中首先导入torch(拓展库中有依赖关系),即 import torch
没有找到ninja:UserWarning: Attempted to use ninja as the BuildExtension backend but we could not find ninja. Falling back to using the slow distutils backend. warnings.warn(msg.format('we could not find ninja.'))
sudo apt-get install ninja-build
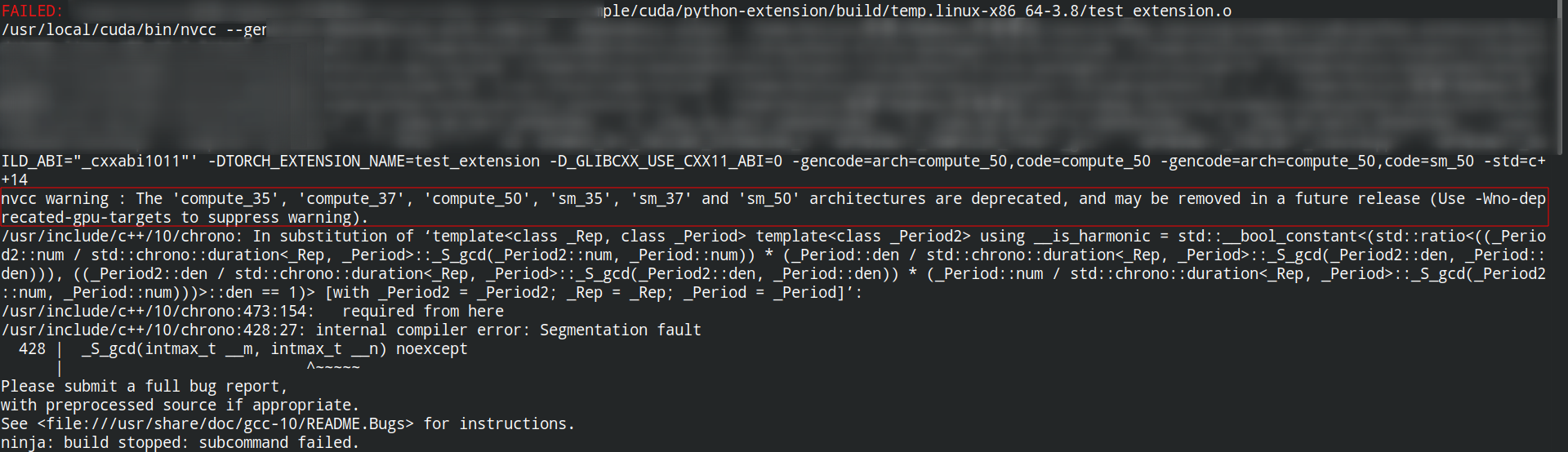
The 'compute_35', 'compute_37', 'compute_50', 'sm_35', 'sm_37' and 'sm_50' architectures are depre cated, and may be removed in a future release:无法编译通过。一种解决方案是调整cuda的版本(未实测);一种是使用sm>50的GPU
性能优化
instrument-level
数学运算
使用右移运算符来取代除法和求余(能生成更少的指令)

循环数使用有符号整型(编译器能进一步进行优化代码)

Q&A
为什么线程块中的线程数尽量设计为32?

GPU指令的执行是以一个block中的32个线程(called warp)为执行单位的;指令执行总数 = 一个线程/一个warp将要执行的指令数 × warp数;不同线程的组织方式,warp的数量也不同。
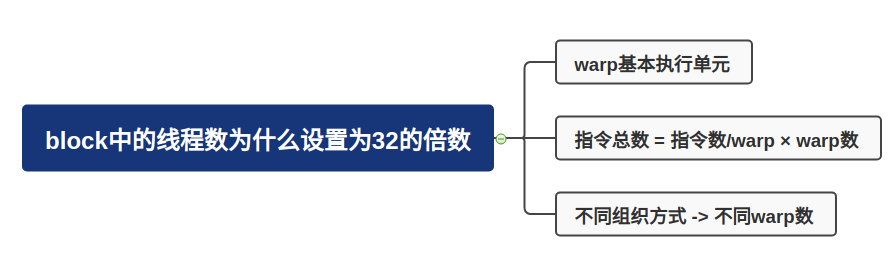
比如说有384个线程,每个线程要执行10个指令。可以分配8个线程块,每个线程块48的线程,其对应160个指令;另一方面也可以分配64个线程块,每个线程块6个线程,其对应为640个指令。所以前者的效率会更高。
nvidia硬件层级解读#Hardware_perspective)
GPU由多个SM组成。一个SM能处理多个block。当一个SM接收到一个block时,首先将它们划分为一个warp。处理完一个block再处理下一个block。
为了并行执行成百上千的线程,SM采用了SIMT的架构

显卡计算能力
version number:显卡计算能力用version number来表征。其中首位数字表征框架,如8对应安培架构,7对应伏打架构;第二位数字表征更多的特性。比如图灵架构(7.5)是伏打架构(7.0)的升级版。
cuda流如何加速应用程序

(1)理解流水线前传机制,该机制如何使cpu效率显著增加
(2)CPU的三级缓存的特点,哪些内容适合放在哪一级别的缓存上
(3)什么样的问题适合GPU,结合日常编程的任务 .. image:: https://natsu-akatsuki.oss-cn-guangzhou.aliyuncs.com/img/zBugODGh3u7sqNHY.png!thumbnail
(1)GPU控制单元和计算单元是如何结合的?或者说线程束是如何在软件和硬件端被执行。为什么说线程束是执行核函数的最基本单元。
opinion
函数拷贝数=线程块个数 p43
线程块越多越好还是线程越多越好? P43
在实际测试中,为什么线程块中的线程超过1024后并没有直接的报错(如:段错误)
一个SM管理32个线程,这32个线程称为warp
GPU控制单元简单,没有分支预测和数据转发
GPU和CPU的区别?前者是以吞吐量(单位时间内执行更多的指令)为导向;后者是以时延(执行一条指令的时间)为导向
API
CUDA设备
cudaSetDevice(int device);
参考资料
分配锁页内存(page-locked host memory)
学习cuda流,用cuda流(stream)来加速应用程序
cuda流是一个内存队列,所有的cuda操作(kernels,内存拷贝)都在流上执行
cuda流有两类,一种是显式流(同步执行),一种是隐式流(异步执行)